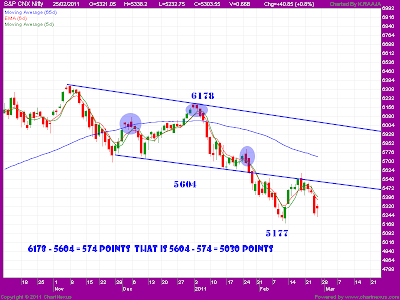
HELLO FRIENDS, HERE IS THE NIFTY SPOT EOD CHART.. ACCORDING TO CHARTS.. THERE IS A FORMATION OF HEAD AND SHOULDERS PATTERN.. WHICH LEADS NIFTY TO 5050 TO 5030 LVLS.. BUT NIFTY NOT COMPLETED ITS FULL TURN UPTO 5030 LVLS... SO ACCORDING TO PATTERN FORMATION.. NIFTY STILL NEEDS TO TEST LOWER LVLS TO MAKE PATTERN FULLFILL.. IS DOWN FALL IN NIFTY STILL EXIST ?
Saturday, February 26, 2011
Thursday, February 24, 2011
A Case of investing in Silver
A Case of investing in Silver
SILVER, the poor cousin of gold has been on a roll.
Also, silver prices have been on all time high levels, and currently
Take the case of 58-year old Usha Joshi, who always wanted to
At the opportune time, plans to gift these precious metals to her
So, What's The Silver Story?:
Silver, unlike gold, has a lot of industrial uses. Silver is the best
Buy silver for the long term, and has a target of 60,000 per kilo
Given this analysts, expect silver prices to appreciate faster than gold.
In the short term, silver prices could see a correction.
However, for retail investors it is very difficult to time the market
With white metal likely to become extinct by 2020,
the next decade may very well see it outshine gold
SILVER, the poor cousin of gold has been on a roll.
Since the beginning of this year, the metal has given a whopping
61% returns. Gold in the same period has given a return
of around 15%.
Also, silver prices have been on all time high levels, and currently
quote at 44,130 per kg. Despite these all-time high levels, buying silver
seems to be catching on in India.
Take the case of 58-year old Usha Joshi, who always wanted to
buy silver. However, the idea of holding silver physically seemed
problematic to her. While she could buy gold through exchange
traded funds (ETFs), she could not do the same in case of silver,
as no silver ETFs are available in India. However, now she has a
solution to her problem. She buys both e-gold and e-silver through
the National Spot Exchange, where it is possible to buy silver in lots
of 100 grams and gold in lots of 1 gram.
At the opportune time, plans to gift these precious metals to her
grandchildren. It's easier than going to a jewellery shop.
So, What's The Silver Story?:
Silver, unlike gold, has a lot of industrial uses. Silver is the best
conductor of electricity, the best heat transfer agent, the best
reflector of light, a marvellous lubricant and a versatile catalyst
and alloy. Other than these properties silver, after gold, is also
the most ductile and malleable. Silver has industrial value and finds
use in dentistry, photography and motherboards.
The demand for these industrial products is on the rise. Besides that,
the global recession has taught people to go beyond paper assets
and invest in precious metals. Hence the recent interest in gold
and silver.
Buy silver for the long term, and has a target of 60,000 per kilo
with a three-year timeframe. What is also not too well known is that
there is less silver on earth than gold. There is less silver bullion in
the world than gold bullion inventory. The shocking thing is how
few people are aware that silver is rarer than gold." He estimates
that global silver inventories have fallen to around 1 billion ounces
(one troy ounce equals 31.1 grams). In comparison there are 5 billion
ounces of gold available around the world. Of course, Butler is very
optimistic on the price of silver.
The Technical Reason:
Silver moved in a band of $10 to $21 per ounce, for a long period from
The Technical Reason:
Silver moved in a band of $10 to $21 per ounce, for a long period from
2007 to 2010. It broke that band after a long time, which makes me
bullish on the metal. He feels that within two to three years, globally
silver could reach $50 per ounce against the current price of $28.4
per ounce, while in India, it could reach 55,000 per kilo from current
levels of around 44,000 per kilo. The rationale for a lower rise in silver
in terms of Indian rupees is due to the fact that Banthia expects the
rupee to strengthen and go up to 42 per US dollar, limiting the gains
in rupee terms.
Gold Versus Silver:
The investment argument of silver is pretty simple. The various industrial
Gold Versus Silver:
The investment argument of silver is pretty simple. The various industrial
uses of silver are growing and there isn't enough silver going around to
satisfy that demand. Adrian Douglas, the proprietor of Market Force
Analysis, and also a director of GATA (the Gold Anti-Trust Action
Committee), said in a recent interview that the world will run out of
silver in 2020, and thus silver will become the first element from the
periodic table to become extinct.
Given this analysts, expect silver prices to appreciate faster than gold.
As global uncertainty fades and industrial activity picks, I expect higher
demand for silver, so it could move faster than gold.
In the short term, silver prices could see a correction.
However, for retail investors it is very difficult to time the market
and it is best that they accumulate it over a long term. Retail investors
should systematically buy gold and silver every month.
This could constitute up to 10% of your total investment portfolio.
How To Buy Silver:
Of course, the traditional way to buy silver is buying it from your
How To Buy Silver:
Of course, the traditional way to buy silver is buying it from your
jeweller. Traditionally, individuals are used to buying coins or silver bars.
Some even buy ornaments, while some families also buy silver utensils.
However, there are a couple of problems in buying coins and bars.
First is that of purity and
Second is of storing it. Silver is bulkier than gold and needs
more storage space.
So, storing bars can be a problem. Physical silver is typically more
bulky and investors sometimes face this storage problem for larger
quantities. This increases the cost of storage and may be the cost
of insurance too. Though smaller investors can easily manage the
storage as a typical 1 kg silver bar would be 99 x 49 x 22 mm in size.
It is not practical to buy 20 kg as an investment — firstly to store
it is cumbersome and secondly, purity may be an issue in some cases.
Also, normally I need to sell it back to the same merchants so that
they recognise the purity. More than that, there is that wealth tax
that has to be paid on physical silver.
While there are a lot of gold ETFs, silver ETFs have not been allowed
as yet. So, how does one buy it for investment? The most practical
solution is to buy e silver. E silver has been launched recently by
National Spot Exchange.
According to brokers, about 30 to 40 crore of silver is traded on a
daily basis, thus giving enough liquidity for retail investors.
This is the same way as you buy shares and they are held in
dematerialised form. In case you want physical silver, you can do
the necessary paperwork with the depository participant and collect it.
However, currently there are limited centres which could be a barrier
for investors. For example, if you stay in Hyderabad, it may not be
feasible to take possession of physical silver as the delivery centres
of National Spot Exchange are located in Mumbai, Delhi and Ahemdabad.
So, go ahead and buy e silver to ride the white metal boom, keep it as a hedge
against inflation or pass it on to your next generation.
dematerialised form. In case you want physical silver, you can do
the necessary paperwork with the depository participant and collect it.
However, currently there are limited centres which could be a barrier
for investors. For example, if you stay in Hyderabad, it may not be
feasible to take possession of physical silver as the delivery centres
of National Spot Exchange are located in Mumbai, Delhi and Ahemdabad.
So, go ahead and buy e silver to ride the white metal boom, keep it as a hedge
against inflation or pass it on to your next generation.
source email
INTRADAY CALLS ON 24TH FEB 2011
BUY ACC ABOVE 1016.30 SL 1012 TGT 1020..1024...1028..1032
SELL ACC BELOW 1012 SL 1016.30 TGT 1008..1004..1000...996
BUY UNITECH ABOVE 35.70 SL 35 TGT 36 ... 36.70.. 37 ..37.50
SELL UNITECH BELOW 35 SL 35.70 TGT 34.60..34.20..33.80
BUY HEROHONDA ABOVE 1478 SL 1472 TGT 1487..1491 ...1496...1501
BUY MANINFRA ABOVE 175 SL 173 TGT 180 ++
Wednesday, February 23, 2011
FINANCIAL MARKETS
Financial Markets
- Session One
Every country is built on a certain economy; controlling, managing, sustaining is the main major role of an economy; Economy means the largest set of inter-related economic production and consumption activities which aid in determining how scarce resources are allocated.
Each economy must encompass every single detail that is related to the production and consumption of goods and services in a certain allocated area, trying to sustain it in a way that might help to prosper and develop certain sectors.
In each economy there are two different types of policies; fiscal and monetary policy:
The fiscal policy: is a policy stimulated by the policy makers, it is divided into taxation law and government spending; the government can adjust these laws in order to modify the amount of non-refundable income available to its tax payers, for example a government could ask more taxes from individual which makes them have less amount of money used in spending on goods and services, then the government could use those money to inject it back again into certain companies and markets by something called Government Spending. The higher the government spending means that they are going to demand more taxes from individuals in the economy; but the major disadvantage of this policy is that it might take time in order to achieve all that.
The Monetary Policy: is the second type of polices used in managing a certain economy, this type of policy is mainly controlled by central banks, meaning that they control the supply of money into the economy, by putting cost on the borrowing of these money with some thing called Interest Rates. Interest rates are defined as the percentage amount of money charged on borrowed or lent money, as it could be variable or fixed.
Another classification to an economy is, open and closed economy; an open economy means that it has bilateral trade with other economies all around the world for example the United States. A closed economy has a limited regulated trade with other world economies like china.
Inside each economy there is a Financial System; Financial System is “found to organize the settlement of payments, to raise and allocate finance and to manage the risks associated with financing and exchange; developed to secure efficient payment system, security markets and financial intermediaries that arrange financing and derivative markets and financial institutions that provide access to risk management instruments”.
There are two major roles of a financial system; the first one is to organize surplus funds from people and organizations, and to reallocate them into deficit facing organizations or people; as those mobilized funds are used to generate returns for the surplus entities, by enabling deficit entities to augment their productive and purchasing capacities.
A financial system contains something called financial markets; a financial market is a mechanism that allows people to easily buy and sell financial securities, commodities, and other fungible items of value at low transaction costs and at prices that reflect efficient market hypothesis.
Securities: “essentially a contract that can be assigned a value and traded”.
Commodities: “ a tangible good, or product that are subject of sale or barter, such as grains, metals, and foods traded on commodities exchange or on spot market”.
Fungible: “it is a specified type of commodities; it is defined with a certain type of good that must be given without any changes in the contract”.
Transaction cost: “cost incurred when buying or selling securities, which includes commission and spreads (the difference between the prices the dealer paid for a security and the prices at which it can sold)”.
Efficient Market hypothesis: “means that each share price in a market must reflect all relevant information".
- Session Two
Investor is a person who invests in any different type of markets, for example equities, commodities derivatives, currencies, real estate; as this term is connected with the individual who is looking for profit from a certain investment. Types of investors' can be classified on certain criterion which is known by risk (the possibility of suffering damage or loss).
Risk is calculated by dividing the standard deviation over the historical average returns.
Risk = Standard Deviation /Average Returns
Speculators:
Are type of investors' who take higher than average risks, seeking for abnormal profits, as they are mainly concerned about speculating which might be the futuristic prices of a certain asset e.g. currency or a commodity; mainly they are involved in buying and selling future and option contracts in the short term, as they represent almost 70% if investors'; which might be known by "Risk Seekers".
Hedgers:
Are types of investors' who tries to avoid or cancel any risks that can be accompanied with certain investment, they try to take positions that might prevent them from any potential losses, these types of investors' are widely found in markets that are full of uncertainties and high volatility. There are many types of hedging positions like natural hedges, hedging credit risk, hedging currency risk, hedging equity and equity futures. Which are also known by "Risk Neutrals".
Arbitragers:
Are types of investors' who buy securities in one market then immediately resell it in another market in order to profit from prices divergence, as this type of dealing is only suggested only for well experienced investors' as any delay in transactions could result of huge losses; the effect of these transaction would result in adjusting price differences between markets.
Markets:
There are three types of markets
Factor market: it is the types of markets that include all features of production for example land, labor, capital.
Product market: is the market that includes all distributing products like food, goods and services.
Financial markets:
Types of financial markets
Primary market: type of market that only sells the newly issued securities.
Secondary market: it’s a market where buyers buy from the seller rather than getting it from issuing company.
Over the counter market (OTC): it’s a type of market that trades occur via phone or a network instead of a physical trading. Those types of markets are found for companies that do not meet the exchange listing requirements. Inside the OTC market there are:
- Market makers: it’s a type of firm that takes in a certain type and number of shares in order to ease the trading in this security, each market maker displays buy and sell quotations for a certain number of shares, when the order is set the market maker instantly sells from his inventory, as this transaction takes only a small amount of time; for example NASDAQ is considered to be a market maker. The market maker profits from the spread, which is the difference between the prices for buying and the prices at which they are willing to sell at.
- Ask prices: is the price the seller is willing to take for a certain type of security and besides the ask prices their will be the amount of securities the market maker is willing to sell; which are also known by the Bears.
- Bid prices: the prices the buyer is willing to take, which is the opposite of the ask prices, the bulls in the markets are known by the bidders.
Money Market: is a type of market instruments that mature in less than one year as they are very liquid, the instruments involved in this market have fixed income and low risk for example treasury bills and commercial papers.
Capital Market: it’s a market of trading more risky instruments with a longer maturity date, as this market consists of the primary and the secondary markets.
Bond market: "the place were the issuance and the trading of the debt securities occur", as most bond market instruments are traded in the OTC market.
Stock market: is the market in which shares are traded through exchange floor or over-the-counter, which is known by another name equity market, this market helps investors' to have a partial ownership in a certain company, and some gains or dividends based on the company's performance.
A stock is defined as share of ownership in a certain company, and the more stocks you obtain the bigger your share in the company, which is confirmed by a certain piece of paper called a certificate. The managers of a company are supposed to increase the value of those investments to increase the confidence of investors' in the company to raise its share price.
There are two types of stocks, preferred and common stocks. A common stock are type of shares that are released to public were any body can acquire; a preferred stocks are another type of stocks that are sold to certain people, not publicly available. The difference between both types of stocks is that preferred stocks have the priority in taking distributed dividends and in the liquidation of the company.
Functions of Financial marketsBorrowing and lending: financial markets provides money to investors', by giving out certain amount of money but with certain interests which is known by cost of borrowing.
Price determination: sets or defines fixed or volatile prices for each type of instrument in the market.
Information collection and analysis: provides information for market participants to value or estimate prices of a certain instrument.
Risk sharing: financial markets eliminate a type of risk known by systematic risk, by diversifying investments.
Liquidity: markets provide sufficient amount of buyers and sellers helping any investors' to directly convert instruments into cash.
Efficiency: markets reflecting all the publicly available information on a certain instrument.
Major market participant
Broker: a broker's job is to locate a buyer to the seller, as they involve in assets transformation.
Dealer: smoothes the process of matching the buyer with the seller.
Investment banks: contributes in selling the newly issued securities.
Financial intermediaries: They are foundations that act as mediator between investors and firms.
- Session Three:
Are type of securities that their value is abstracted from other financial instruments; these types of derivates are used as a hedging bargain to stop any losses from any reversal movement in the market, so the main use is to "Control Risk"; it is mainly used with currency and interest rates.
The derivative is used by the three types of investors:
Hedgers: the Hedger uses the derivates in order to minimize the losses by taking a position opposite to the transaction that he/she is having, so if the market reverse no major losses will occur.
Speculators: the speculator will get in market just looking for abnormal profits, with accepting higher risk, by taking an open position.
Arbitragers: the arbitrager try's to look for low risk profit, by taking advantage of difference in prices.
A derivative includes different types of instruments:
Forward Contracts: are negotiated between two parties, to buy a long position and sell a short position of a specified amount of a commodity, as the buyer hold the right to undertake the action but not obligated, and setting the price (known by the spot price) of the commodity at a specified date.
Future Contracts: are standardized contracts that are traded on a regulated floors, obligating the delivery of the agreed amount of commodity or a currency or an instrument for example treasury bonds, foreign currency. These types of contracts are considered to have low risk.
Options: is a contract that designed to specify in it the quantity of a certain commodity with the specified date of transaction, were options have the right to buy or sell but not the obligation.
There are two types of option contracts:
Call option: gives the buyer the right to buy (but not the obligation) a specified amount of securities at a certain price at a set date.
Put option: gives the buyer the right to sell (but not the obligation) to the writer of the option by a certain prices and a specified date.
Swaps: "is a flexible, private, forward-based contract or agreement, which is used to hedge against exchange risk from mismatched currencies on assets and liabilities.
There are different types risk associated with derivatives:
Basis risk: it is the price of the hedged asset subtracted from it the price of the derivative contract.
Credit risk: it's the risk of the chance of one party offsetting the financial obligation under the contract.
Market risk: it's the loss due to changes in the value of the derivative, including different types of risks control, accounting and legal risks.
- Session Four:
Depth:
Market depth is defined as the capability of the market to generate enough or extra orders without having an affect on the price of a security, as it can be defined in another way, it is measured also with the liquidity, the more liquid the markets are the more depth it has; moving security prices in large markets is really hard, because of the depth of the markets large orders must be taken in order to change prices slightly.
There are certain factors which affect market depth:
Tick Size
Prices movement restriction
Trading restriction
Allowable leverage
Market Transparency
But there is a very big role that takes place in the markets that we can't ignore, which is known by investors' rationality, or market psychology.
Markets in general are really built on speculations, forecasts and fears; if certain gossip spreads in markets average investors' would really panic which at the end leads them to take irrational acts, that could really affect the trend that is going into markets, but let's not forget the bigger influential which is known by attitude toward risk.
We all know a rational investor won't really take into consideration any spread of rumors into markets they will concentrate more risk; but the enigma starts when the amount of average investors' in markets gets bigger which would eventually affect the overall movement, obligating rational investors' to take different actions to wipe away any extra risk that can be added on them.
SOURCE ECPULSE
Monday, February 21, 2011
TECHNICAL LEVELS ON 21 FEB 2011
PIRHEALTH
WATCH PIRHEALTH AT 439 LEVELS CAREFULLY, IF BREAKS FALL EXPECTED TILL 437.80 .. 436.80 .. 436 .... BELOW 436 FREE FALL TILL 434.60... 434.. 433.30 ... BELOW THIS WATCH 429 TO 430 LVLS...KEEP STOP LOSS AT 441.50 IN PIRHEALTH IN SHORT SIDE...
AMAR
WATCH AMAR AT 87 LEVELS.. BELOW THIS WILL TEST 85 LEVELS AND 83.80 ..82.80...81.75..80.10.. BELOW 80.10 FREE FALL EXPECTED SHORT BELOW 87 WHILE KEEPING STOPLOSS AT 88.80
DLF
WATCH DLF AT 232 TO 231 LEVELS... CAREFULLY IF BREAKS THESE LEVELS WATCH FREE FALL TILL 228..226.50..223.40...221 KEEP STOPLOSS AT 234.30 IN SHORT SIDE
ABAN
ABAN BELOW 569.30 WEAK WILL TEST 566.20..559..552.30.. BELOW 552.30 FREE FALL TILL 528 WATCH THIS LEVELS IN COMING DAYS ALSO .. KEEP STOPLOSS AT 574 IN SHORT SIDE...
HINDCOPPER
SELL HINDCOPPER BELOW 321 SL 324 TGT 317 ...315 .. 312 ..--
Sunday, February 13, 2011
WEEKEND FUN - COMEDY OF ERRORS...
Reliance A(NIL)-Comedy Of Errors Or A Man Wearing Two Hats?
Anil Ambani has gone to press once more, talking about an invisible bear lobby which is attacking it's stocks and mauling them in the process. He may be right or maybe just underlining the panic that investors are facing today.
A few years ago the Ambani scions split up their father's empire. The younger Mr. Ambani got Power, Telecom and Infra businesses. All ventures were new and hence suspect from profitability point of view.
-Reliance Natural Resources had no business model, except distribute gas from KG6.
-Reliance Communication had CDMA technology which was considered inferior to GSM tech.
-Reliance Energy had the power gen and distribution business of BSES.
-Rcap did nothing except promote the Reliance MF.
What happened since then?
-First, in an attempt to step out of the shadow of his elder brother, Anil created a separate identity as Reliance ADAG group.
-Second, in an attempt to grow he acquired Adlabs, and bid for UMPPs under the subsidiary route of Reliance Energy by creating RPower.
Unfortunately, the younger Ambani lost the claim to KG6 gas and lost the business for RNRL. In a mockery of stock markets and its regulators, RNRL instead of going for liquidation was merged with RPower.
Rcom made an attempt to go GSM, and then created a multitude of businesses by breaking into bits Adlabs into DTH/Movie business and Radio FM into Reliance Media.
RPower made a mega issue 3 years ago amounting to Rs 10000 crore at Rs 450 per share. With no project near commissioning, the stock got ripped. Claims were made and allegations made on rivals. A bonus to non promoter shareholders was made and then RNRL was merged with it.
As things stand no business of RADAG is near fruition, all have long gestation period and stocks which suited VC players should never have been listed. Reliance Energy now named Reliance Infra is offering a Buy-Back.
RADAG has decided to drop ADAG from it's reference point and call itself a Reliance group company. Reliance Infra shares a similar sounding name with Reliance Industrial Infra-owned by his brother. So in all likelihood, instead of distancing from the other Mr. Ambani, Anil Ambani is trying to gain some leeway from his brother's company.
The point is, should promoters be managing stock prices or be responsible in turning good corporate performance. If they cannot, then changing technology, splitting companies, changing business models, doling out bonuses, and offering buy-back will not assuage investors who are seeing their life savings go down the drain.
In the end, the two Ambani's remain billionaires have 40-50 storied homes in Bombay, and the poor remains struggling on the Bombay City Trains. The dreams seem over for those millions.
Finally, why a buy-back of stocks why not just de-listing? And why change names? Why not just wear two hats?
SOURCE EMAIL
SOURCE EMAIL
Egypt's Mubarak Steps Down, Hands Power to Military
Egyptian President Hosni Mubarak, ending 30 years of rule, has resigned and handed over control of the country to the military, Vice President Omar Suleiman announced Friday.
The president "has decided to give up his position as president of the republic," Suleiman said on national TV. He added that the president had charged the higher military council to run affairs in the "tough circumstances that the country is passing through."
After refusing to step down on Thursday, Mubarak finally bowed to a historic 18-day wave of pro-democracy demonstrations by hundreds of thousands.
Stocks rose in reaction to Mubarak's resignation, while oil prices fell .
Prices of gold and U.S. Treasury bonds partly erased early gains as Mubarak's departure partially revived investors' appetite for risk. The U.S. dollar briefly pared gains, but remained strong against a basket of major currencies.
"It looks like the stock market is taking the news well," said Gary Thayer, chief macro strategist with Wells Fargo in St. Louis. "One thing that has weighed on investor sentiment is that the price of oil would go up in the case of political turmoil, and Mubarak's leaving reduces that possibility."
A massive crowd in Cairo's central Tahrir Square exploded into joy, waving Egyptian flags, and car horns and celebratory shots in the air were heard around the city of 18 million in joy after Vice President Suleiman made the announcement just after nightfall.
Nobel Peace laureate Mohammed ElBaradei, whose young suporters were among the organizers of the protest movement, told The Associated Press, "This is the greatest day of my life." "The country has been liberated after decades of repression," he said adding that he expects a "beautiful" transition of power.
Earlier Friday, a ruling party official told Reuters Mubarak and his family had left Cairo for the glitzy Red Sea resort of Sharm el-Sheikh where there is a presidential residence, adding that this proved that power had been handed to Suleiman.
Mubarak had sought to cling to power, handing some of his authorities to Suleiman while keeping his title. But an explosion of protests Friday rejecting the move appeared to have pushed the military into forcing him out completely.
Hundreds of thousands marched throughout the day in cities across the country as soliders stood by, besieging his palace in Cairo and Alexandria and the state TV building.
A governor of a southern province was forced to flee to safety in the face of protests there.
It was the biggest day of protests yet in the upheaval that began Jan. 25, growing from youth activists working on the Internet into a mass movement that tapped into widespread discontent with Mubarak's authoritarian lock on power, corruption, economic woes and widespread disparities between rich and poor.
Outside Mubarak's Oruba Palace in northern Cairo, women on balconies ululated with the joyous tongue-trilling used to mark weddings and births.
"Finally we are free," said Safwan Abo Stat, a 60-year-old in the crowd of protesters at the palace.
"From now on anyone who is going to rule will know that these people are great." Another, Mohammed el-Masry, weeping with joy, said he had spent the past two weeks in Tahrir before marching to the palace Friday.
He was now headed back to the square to join his ecstatic colleagues. "We made it," he gasped.
The question now turned to how the military, Egypt's most powerful institution, will handle the transition in power.
Earlier in the day, the Armed Forces Supreme Council—a body of top generals—vowed to guide the country to greater democracy.
In a statement hours before Suleiman's announcement, it said it was committed "to sponsor the legitimate demands of the people and endeavorfor their implementation within a defined timetable ...until achieving a peaceful transition all through a democratic society aspired by the people."
Abdel-Rahman Samir, one of the youth organizers of the protests, said the protest movement would now open negotiations with the military over democratic reform but vowed protests would continue to ensure change is carried out.
"We still don't have any guarantees yet _ if we end the whole situation now the it's like we haven't done anything," he said.
"So we need to keep sitting in Tahrir until we get all our demands." But, he added, "I feel fantastic....I feel like we have worked so hard, we planted a seed for a yera and a half and now we are now finally sowing the fruits."
Wednesday, February 9, 2011
TRADING SYSTEMS........
1.Commodity Channel Index Trading System
Required Indicators:
CCI indicator
CCI Control Level (user-defined); default value is +40, -40
CCI Extreme Level (user-defined); default value is +100, -100
Entry-Exit Conditions
Long Entry: CCI crossing above CCI control level (+40)
Long Exit: CCI crosses above CCI extreme level (+100), then exit when CCI crosses below CCI control level (+40)
or
CCI never crosses above CCI extreme level (+100), then exit when CCI crosses below 0
Short Entry: CCI crosses below negative CCI control level (-40)
Short Exit: CCI crosses below negative CCI extreme level (-100), then exit when CCI crosses above negative CCI control level (-40)
or
CCI never crosses below negative CCI extreme level (-100), then exit when CCI crosses above 0
2. Complex Trading System
Type: Always in the market trading system
Required Indicators:
Short Moving Average
Long Moving Average
Relative Strength Indicator
MACD
Entry
Long Entry Conditions:
1. short moving average > long moving average
2. rsi > 50
3. MACD fast line > MACD signal line
Long Exit Conditions:
1. short moving average < long moving average
2. rsi < 50
3. MACD fast line < MACD signal line
Short Entry Conditions:
1. short moving average < long moving average
2. rsi < 50
3. MACD fast line <MACD> long moving average
2. rsi > 50
3. MACD fast line > MACD signal line
3. Channel Strategy
Required Indicators: Trend Lines
Recommended Trading Environment: Prior to fundamental market event or when used prior to open of major financial market
Rules for a long trade (rules for short trade are opposite):
1. Identify a channel on intraday or daily chart; the price should be contained within a narrow range
2. Enter long as the price breaks above the upper channel line
3. Place a stop just under the upper channel line
4. Trail your stop higher as the price moves in your favor
Perfect Order
Required Indicators: Moving Averages (minimum of 5; ie: 10-day SMA, 20-day SMA, 50-day SMA, 100-day SMA, 200-day SMA)
Trading Environment: Trending environment near the beginning of the trend
Condition Required: Moving Averages need to be in perfect order or in sequential order. For example, in an uptrend, a perfect order would be when 10-day SMA > 20-day SMA > 50-day SMA > 100-day SMA > 200-day SMA
Rules:
1. Find currency pair with MA’s in perfect order
2. Look for ADX pointing upwards, ideally greater than 20
3. Buy 5 candles after the initial formation of the perfect order
4. The initial stop is the low on the day of the initial crossover for longs and the high for shorts
5. Exit the position when the perfect order no longer holds
4. Bollinger Bands of Ultimate Oscillator System
Type: Always in the market trading system
Required Indicators:
Ultimate Oscillator
Bollinger Bands based on the Ultimate Oscillator
Moving Average of the Ultimate Oscillator
Entries
Long Entry: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses above the middle bollinger band
Long Exit: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses below the Middle bollinger band
Short Entry: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses below the middle bollinger band
Short Exit: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses above the middle bollinger band
5. SIMPLE MACD SYSTEM...
Type: Always in the market trading system[/color]
Required indicators: MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Entries
Long Entry: MACD Fast Line crossing above the MACD signal line
Long Exit: MACD Fast Line crossing below the MACD signal line
Short Entry: MACD Fast Line crossing below the MACD signal line
Short Exit: MACD Fast Line crossing above the MACD signal line
IF YOU HAVE ANY DOUBTS, YOU CAN POST HERE..
Required Indicators:
CCI indicator
CCI Control Level (user-defined); default value is +40, -40
CCI Extreme Level (user-defined); default value is +100, -100
Entry-Exit Conditions
Long Entry: CCI crossing above CCI control level (+40)
Long Exit: CCI crosses above CCI extreme level (+100), then exit when CCI crosses below CCI control level (+40)
or
CCI never crosses above CCI extreme level (+100), then exit when CCI crosses below 0
Short Entry: CCI crosses below negative CCI control level (-40)
Short Exit: CCI crosses below negative CCI extreme level (-100), then exit when CCI crosses above negative CCI control level (-40)
or
CCI never crosses below negative CCI extreme level (-100), then exit when CCI crosses above 0
2. Complex Trading System
Type: Always in the market trading system
Required Indicators:
Short Moving Average
Long Moving Average
Relative Strength Indicator
MACD
Entry
Long Entry Conditions:
1. short moving average > long moving average
2. rsi > 50
3. MACD fast line > MACD signal line
Long Exit Conditions:
1. short moving average < long moving average
2. rsi < 50
3. MACD fast line < MACD signal line
Short Entry Conditions:
1. short moving average < long moving average
2. rsi < 50
3. MACD fast line <MACD> long moving average
2. rsi > 50
3. MACD fast line > MACD signal line
3. Channel Strategy
Required Indicators: Trend Lines
Recommended Trading Environment: Prior to fundamental market event or when used prior to open of major financial market
Rules for a long trade (rules for short trade are opposite):
1. Identify a channel on intraday or daily chart; the price should be contained within a narrow range
2. Enter long as the price breaks above the upper channel line
3. Place a stop just under the upper channel line
4. Trail your stop higher as the price moves in your favor
Perfect Order
Required Indicators: Moving Averages (minimum of 5; ie: 10-day SMA, 20-day SMA, 50-day SMA, 100-day SMA, 200-day SMA)
Trading Environment: Trending environment near the beginning of the trend
Condition Required: Moving Averages need to be in perfect order or in sequential order. For example, in an uptrend, a perfect order would be when 10-day SMA > 20-day SMA > 50-day SMA > 100-day SMA > 200-day SMA
Rules:
1. Find currency pair with MA’s in perfect order
2. Look for ADX pointing upwards, ideally greater than 20
3. Buy 5 candles after the initial formation of the perfect order
4. The initial stop is the low on the day of the initial crossover for longs and the high for shorts
5. Exit the position when the perfect order no longer holds
4. Bollinger Bands of Ultimate Oscillator System
Type: Always in the market trading system
Required Indicators:
Ultimate Oscillator
Bollinger Bands based on the Ultimate Oscillator
Moving Average of the Ultimate Oscillator
Entries
Long Entry: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses above the middle bollinger band
Long Exit: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses below the Middle bollinger band
Short Entry: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses below the middle bollinger band
Short Exit: Moving Average of Ultimate Oscillator crosses above the middle bollinger band
5. SIMPLE MACD SYSTEM...
Type: Always in the market trading system[/color]
Required indicators: MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Entries
Long Entry: MACD Fast Line crossing above the MACD signal line
Long Exit: MACD Fast Line crossing below the MACD signal line
Short Entry: MACD Fast Line crossing below the MACD signal line
Short Exit: MACD Fast Line crossing above the MACD signal line
IF YOU HAVE ANY DOUBTS, YOU CAN POST HERE..
TYPES OF DIVERGENCES
1.. CLASSIC BEARISH DIVERGENCE
IDENTIFICATION :::
HH PRICE ( HIGER HIGH )
LH INDICATOR ( LOWER HIGH INDICATOR)
INDICATES UNDERLYING WEAKNESS........
WARNING OF A POSSIBLE SHORT TO INTERMEDIATE TERM CHANGE IN TREND FROM UP TO DOWN...

2.. CLASSIC BULLISH DIVERGENCE
IDENTIFICATION ::
LL PRICE ( LOWER LOW PRICE)
HL INDICATOR ( HIGHER LOW INDICATOR)
INDICATES UNDERLYING STRENGTH....
WARNING OF A POSSIBLE SHORT-TO INTERMEDIATE TERM CHANGE IN TREND FROM DOWN TO UP

3. BEARISH HIDDEN DIVERGENCE...
IDENTIFICATION::
LH PRICE ( LOWER HIGH PRICE)
HH INDICATOR ( HIGHER HIGH INDICATOR)
OCCURENCE::
MAINLY FOUND DURING CORRECTIVE RALLIES IN A DOWNTREND..
MAY ALSO OCCUR DURING RETESTS OF A PRICE TOP

4. HIDDEN BULLISH DIVERGENCE...
IDENTIFICATION ::
HH PRICE ( HIGHER HIGH PRICE)
LL INDICATOR ( LOWER LOW INDICATOR)
INDICATION::
INDICATES UNDERLYING STRENGTH..
GOOD ENTRY OR RE-ENTRY...
OCCURES MAINLY DURING CORRECTIVE DECLINES IN AN UPTREND..
MAY BE FOUND ON OCCATION AT PRICE RETESTS OF THE LOWS...

It's about higher highs and lower lows. If you find them in price, but not in the oscillator, you have regular divergence. If you find them in the oscillator, but not in price, then it's hidden divergence.
If the higher highs or lower lows are in price but not the oscillator, then the direction of price is likely to reverse. This is regular, or classic divergence and can be used as a confirming indicator for a reversal entry.
Regular divergence describes a price trend change that will probably happen in the future, albeit shortly. On the other hand, hidden divergence is a confirming indicator of past price direction.
We have hidden divergence when we have higher highs or lower lows in the oscillator but not in price. In this case the direction indicated by higher highs or lower lows in the oscillator is contradicted by the price trend. Unlike regular divergence, where the weakness in price trend is about to lead to a reversal; here the weakness has already led to a little reversal against the trend. The hidden divergence implies that this recent little reversal in price direction will be short-lived and that price will resume moving in the direction of the trend. This is exciting because it can confirm a continuation entry, which is generally much less risky than a reversal entry. What you have here is the opportunity to enter on a pullback of the current trend, which you expect to continue based on this and whatever other indicators you choose. This is trading with the trend, nice and friendly; however, please heed the following warning.
Warning: I consider divergence to be an indicator, not a signal to enter a trade. It would be unwise to enter a trade basely solely on this indicator as too many false signals are given; however, on the other hand, I consider it even more unwise to trade against this indicator.
Regular Divergence:
IDENTIFICATION :::
HH PRICE ( HIGER HIGH )
LH INDICATOR ( LOWER HIGH INDICATOR)
INDICATES UNDERLYING WEAKNESS........
WARNING OF A POSSIBLE SHORT TO INTERMEDIATE TERM CHANGE IN TREND FROM UP TO DOWN...

2.. CLASSIC BULLISH DIVERGENCE
IDENTIFICATION ::
LL PRICE ( LOWER LOW PRICE)
HL INDICATOR ( HIGHER LOW INDICATOR)
INDICATES UNDERLYING STRENGTH....
WARNING OF A POSSIBLE SHORT-TO INTERMEDIATE TERM CHANGE IN TREND FROM DOWN TO UP

3. BEARISH HIDDEN DIVERGENCE...
IDENTIFICATION::
LH PRICE ( LOWER HIGH PRICE)
HH INDICATOR ( HIGHER HIGH INDICATOR)
OCCURENCE::
MAINLY FOUND DURING CORRECTIVE RALLIES IN A DOWNTREND..
MAY ALSO OCCUR DURING RETESTS OF A PRICE TOP

4. HIDDEN BULLISH DIVERGENCE...
IDENTIFICATION ::
HH PRICE ( HIGHER HIGH PRICE)
LL INDICATOR ( LOWER LOW INDICATOR)
INDICATION::
INDICATES UNDERLYING STRENGTH..
GOOD ENTRY OR RE-ENTRY...
OCCURES MAINLY DURING CORRECTIVE DECLINES IN AN UPTREND..
MAY BE FOUND ON OCCATION AT PRICE RETESTS OF THE LOWS...

Divergence Cheat Sheet
It's about higher highs and lower lows. If you find them in price, but not in the oscillator, you have regular divergence. If you find them in the oscillator, but not in price, then it's hidden divergence.
Higher Highs => Short
Lower Lows => Long
At first this seemed to me like the opposite of common sense, so I had to think about it for a while. I finally got it that it means when higher highs or lower lows in either price or an oscillator aren't confirmed by the other, then the direction indicated by the extremes, meaning the higher highs or lower lows, is weak and is likely to change.If the higher highs or lower lows are in price but not the oscillator, then the direction of price is likely to reverse. This is regular, or classic divergence and can be used as a confirming indicator for a reversal entry.
Regular divergence describes a price trend change that will probably happen in the future, albeit shortly. On the other hand, hidden divergence is a confirming indicator of past price direction.
We have hidden divergence when we have higher highs or lower lows in the oscillator but not in price. In this case the direction indicated by higher highs or lower lows in the oscillator is contradicted by the price trend. Unlike regular divergence, where the weakness in price trend is about to lead to a reversal; here the weakness has already led to a little reversal against the trend. The hidden divergence implies that this recent little reversal in price direction will be short-lived and that price will resume moving in the direction of the trend. This is exciting because it can confirm a continuation entry, which is generally much less risky than a reversal entry. What you have here is the opportunity to enter on a pullback of the current trend, which you expect to continue based on this and whatever other indicators you choose. This is trading with the trend, nice and friendly; however, please heed the following warning.
Warning: I consider divergence to be an indicator, not a signal to enter a trade. It would be unwise to enter a trade basely solely on this indicator as too many false signals are given; however, on the other hand, I consider it even more unwise to trade against this indicator.
Regular Divergence:
- Higher highs in price and lower highs in the oscillator which indicate a trend reversal from up to down.
- Lower lows in price and higher lows in the oscillator which indicate a trend reversal from down to up.
- Lower highs in price and higher highs in the oscillator which indicate a confirmation of the price trend which is down.
- Higher lows in price and lower lows in the oscillator which indicate a confirmation of the price trend which is up.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)